
To retain more minerals and water-soluble vitamins, try microwaving, steaming, or baking instead ( 17, 18). Antioxidant capacity: increases by up to 320% with any cooking methodīeta-carotene and other carotenoids increase with some cooking methods because heat breaks down the cell walls in vegetables, allowing it to be released and more easily absorbed ( 16).įor most other nutrients, boiling is the method that reduces nutrient content the most.These seeds were originally a staple food for countries like China, United States, India. Polyphenols: increase by up to 45% with any cooking method Squash seeds are one of the most nutritionally rich vegetable by-products out there, having a high content of unsaturated fat, protein, folate, beta carotene, vitamin C, vitamin B1, fiber, iron, calcium, and potassium.
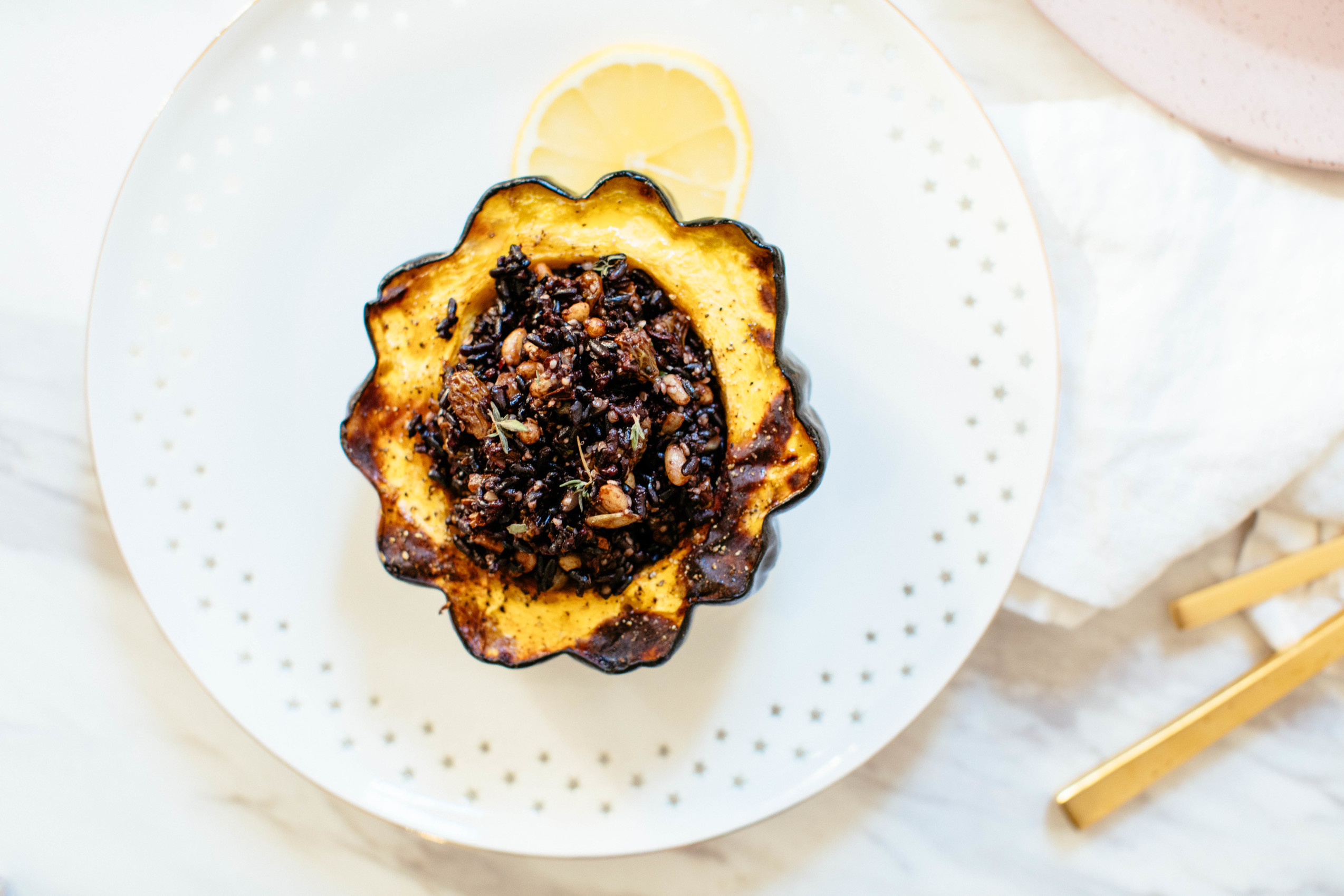

Acorn squash especially abundant in vitamin C, a water-soluble substance that supports immune cell activity and protects against. Although this squash is low in calories, it is high in nutrients. This serving contains 0.2 g of fat, 1.6 g of protein and 22. Acorn Squash Nutrition Facts: Like other winter squash, acorn squash is extremely nutritious, offering a good dose of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Vitamin C: decreases by up to 50% with any cooking method Squash, without salt, mashed, boiled, cooked, acorn, winter contains 83 calories per 245 g serving.Beta-carotene: increases by up to 30% when boiled and decreases by up to 20% when steamed or microwaved.While we didn’t find any studies on acorn squash specifically, research in similar vegetables, such as sweet potatoes, shows how some nutrients are affected by cooking ( 14, 15): Does cooking impact the nutrition of acorn squash?Ĭooking can increase or decrease certain vitamins and minerals in acorn squash, depending on the method used. + Contains carotenoids, but not as much as other winter squashes. There is no official recommendation for carotenoid intake, but some experts suggest getting at least 4 mg of beta-carotene, 0.6 mg of alpha-carotene, and 3.3 mg of lutein daily for general health and reduced risk of lung cancer ( 13). On the other hand, acorn squash provides a small amount of lutein & zeaxanthin (0.053 mg), while sweet potatoes and butternut squash don’t contain any.
#ACORN SQUASH NUTRITION INFO FREE#
Like most winter squash, acorn squash is a rich source of carotenoids, a group of plant pigments that give vegetables their bright red, orange, and yellow colors.Ĭarotenoids have strong antioxidant properties, meaning that they help protect against free radicals - compounds that have been linked to diabetes, heart disease, and cancer ( 7, 8).Ī one-cup (140-gram) portion of raw acorn squash contains the following carotenoids ( 9):Īcorn squash contains less beta-carotene but more lutein and zeaxanthin than similar vegetables, such as sweet potatoes and butternut squash ( 10, 11, 12).įor example, raw butternut squash contains almost 20 times more beta-carotene per cup than acorn squash (5.9 mg vs 0.3 mg, respectively.) + Good source of vitamins B2 (niacin) and B9 (folate) and the minerals potassium and iron.
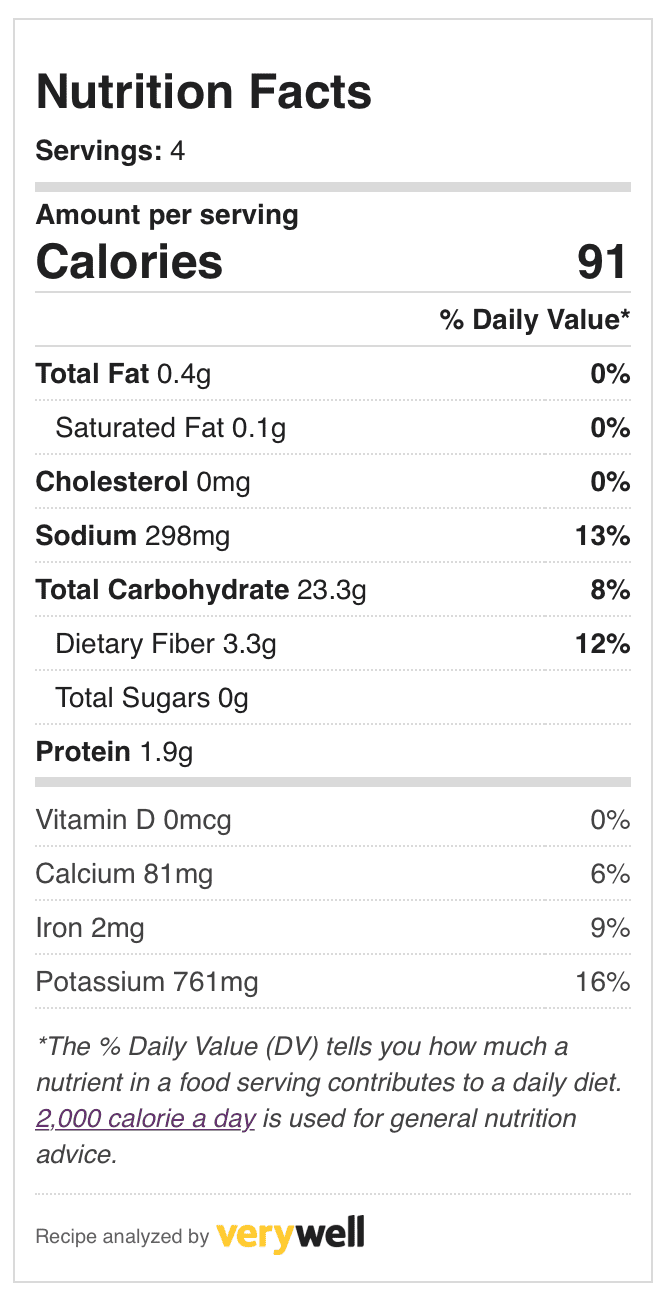
+ Excellent source of vitamins B1 (thiamin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6, and C and the minerals manganese, magnesium, and copper. Calories Protein, 5, (1.6 g x 2.4 Kcal/g 4 kcal) Fat, 2, (0.196 g x 8.37 Kcal/g 1.6 kcal) Carbohydrate, 92, (21.5355 g x 3.6 Kcal/g 76.88 kcal).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
